· Jack Young · Education · 6 min read
Unit 18 (P7, D2): Testing a Relational Database
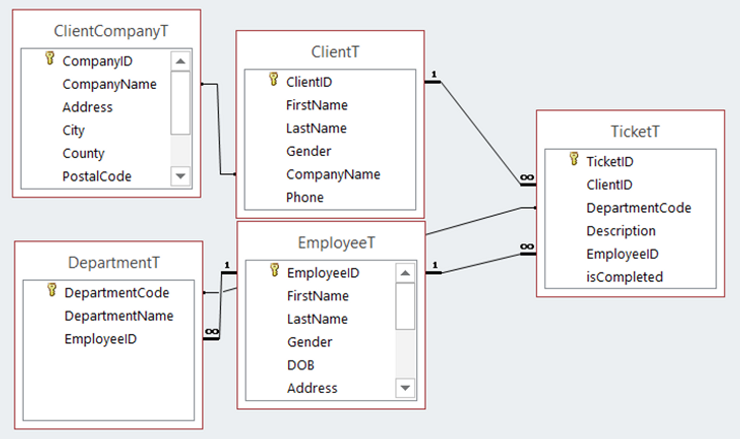
The test plan will give an overview of all the sections of the database I will be testing.
Testing Database
Test a relational database (P7)
Test Plan
The test plan will give an overview of all the sections of the database I will be testing. Here is the test plan:
| Test Name | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|
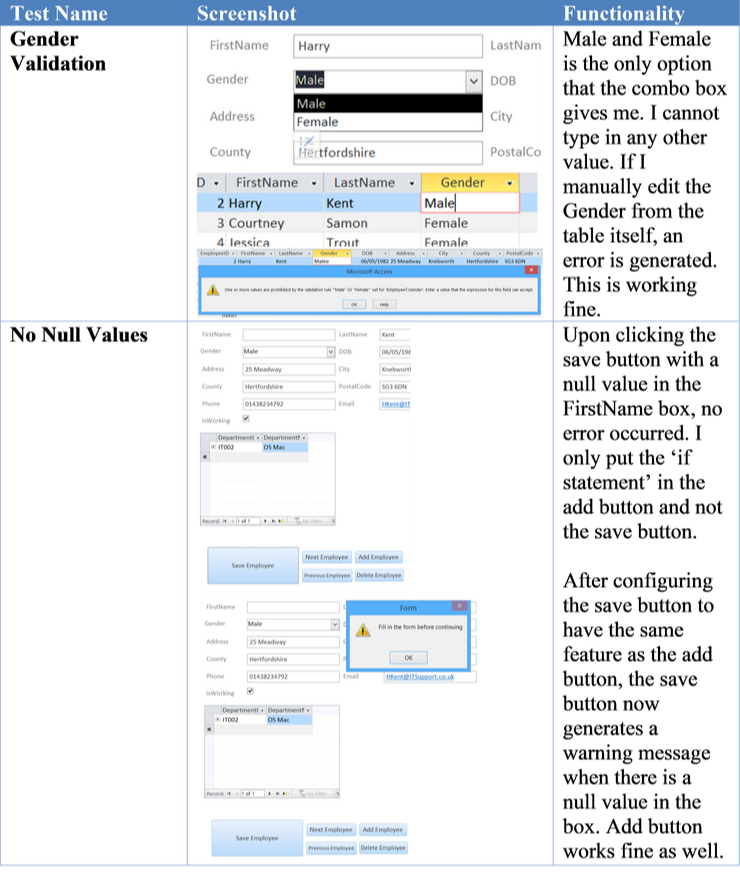
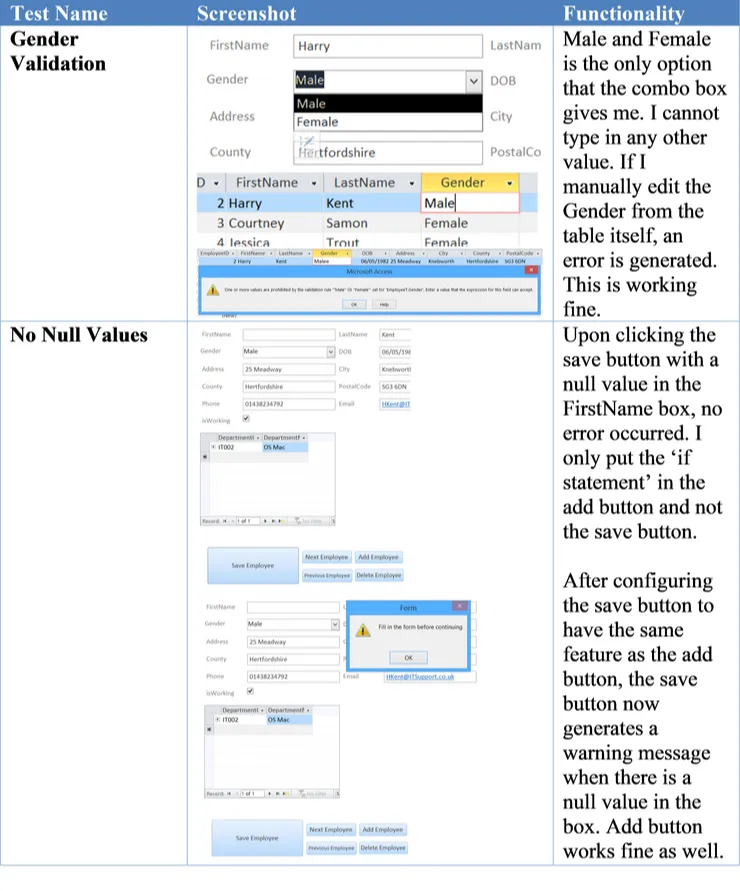
| Gender Validation | Only “Male” and “Female” are able to be entered into the Gender field. |
| No Null Values | When adding records to database, all values in the form should be correctly input. If one value is missing, give a warning and stop the record from being added. |
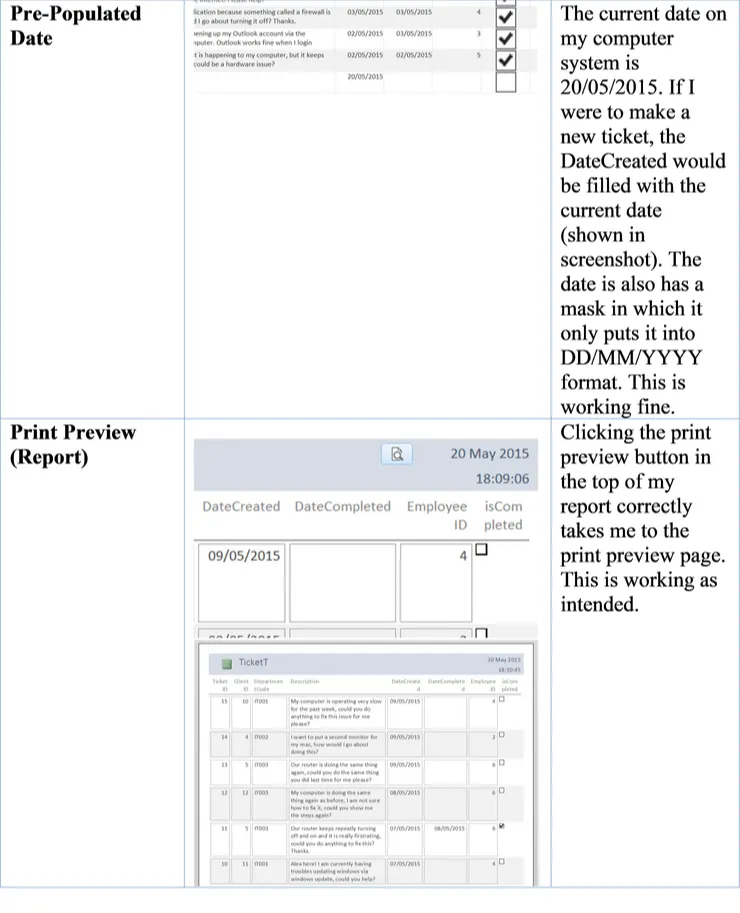
| Pre-Populated Date | Pre-populated date for the ticket should correctly match the current time of the computer system. |
| Print Preview (Report) | Upon clicking the print preview button in the report, it should take me to the print preview page without any errors. |
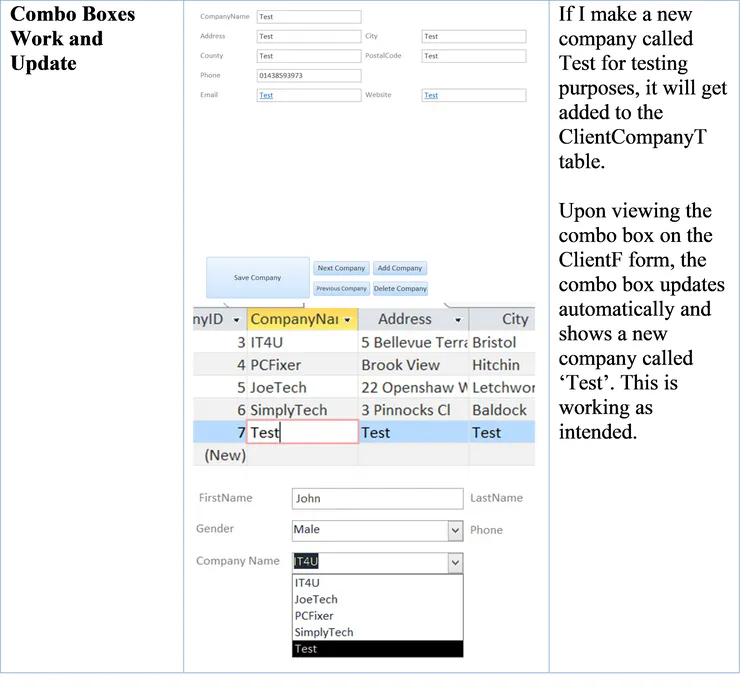
| Combo Boxes Work and Update | When adding a new company to the database, the combo box should correctly match the number of companies with the companies in the combo box automatically. |
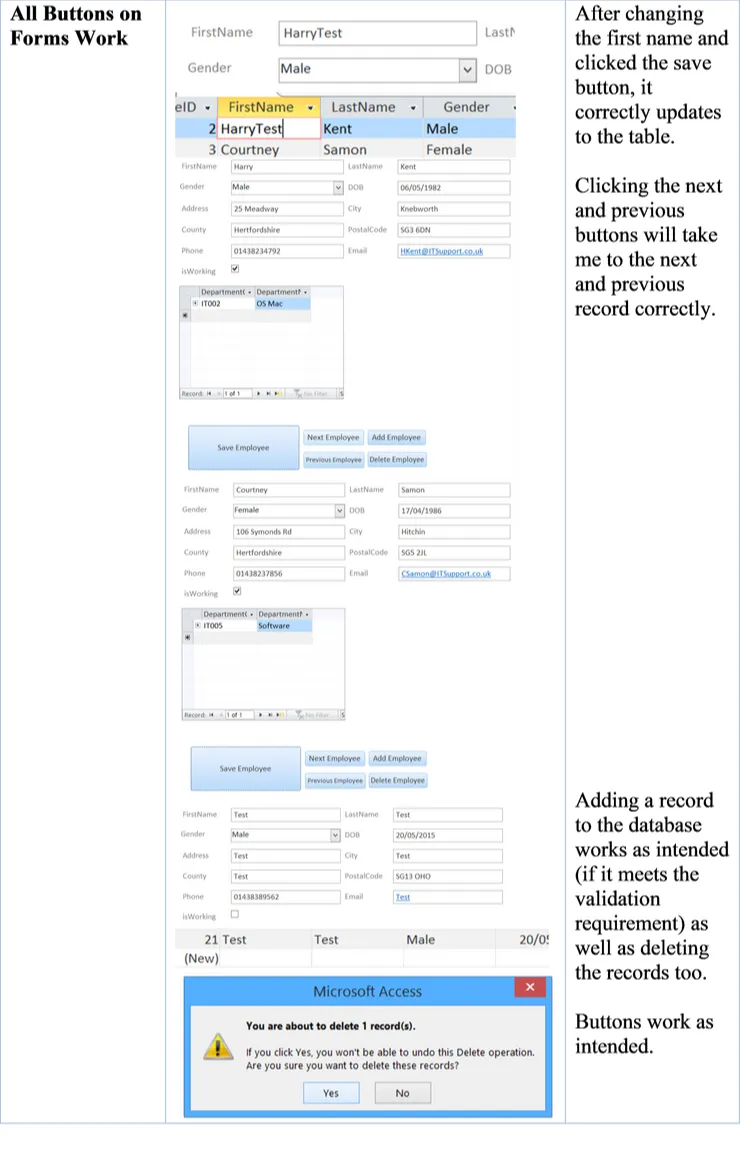
| All Buttons on Forms Work | Save, add, next etc. should work accordingly, if I change a name in a form and click save, it should automatically refresh and update in the tables. |
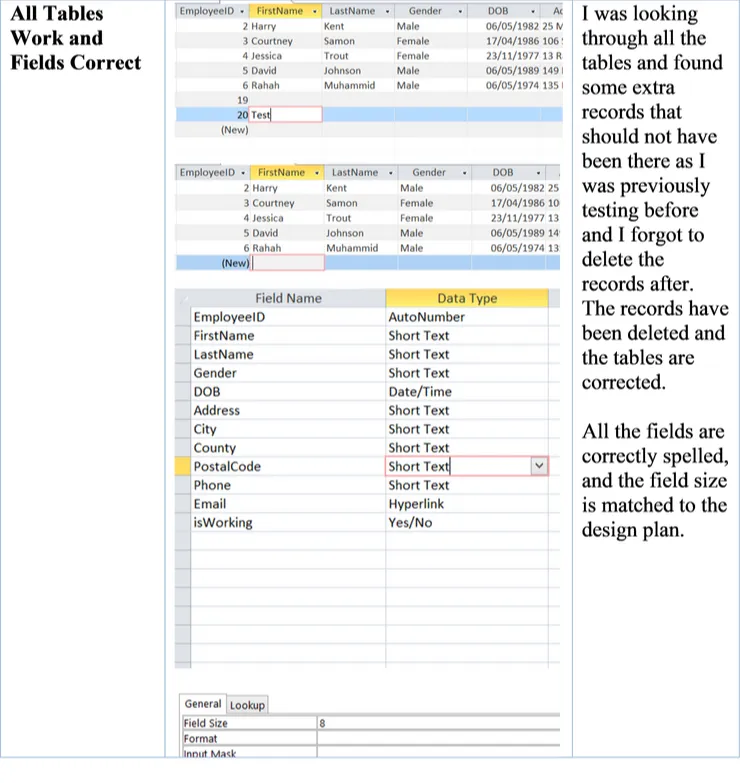
| All Tables Work and Fields Correct | All fields in the tables should have correct spelling and also all the data in the tables are correct. |
Functionality
Following on from the test plan, I test all of these with provided screenshots and to see if the database is functional or not:
Against User Requirements
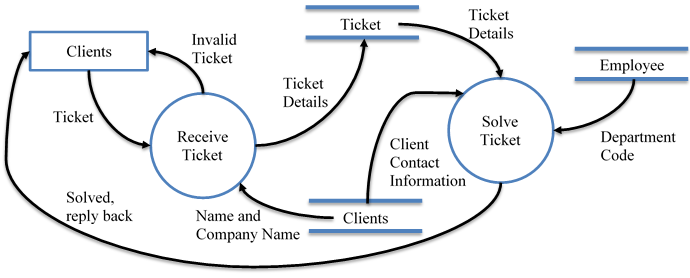
An IT Support company wanted a database that they can list all of their client information so when a client submits a ticket, it displays useful information to help the employee know what company and client quickly.
I have made a good database that suffices the requirements that a small IT Support company would need. I efficiently gave the employees a way to easily view tickets to see what has been done and has not. If the employee wishes to contact to the client for further information, they can grab that from the database easily and know what their phone number is so they can call them immediately. I also made a way for the company to print of reports of the tickets created in the last x amount of days. The company can easily add, delete, save records using a simplistic form that is easily usable for an employee who does not have any knowledge about access or if the company does not want employees modifying the database manually.
I think I have achieved the user requirements in making the database.
Evaluate a Database against the Specified User Need
Evaluate a database against the specified user need (D2)
Fit for Purpose
The purpose of having this database is to easily organise and manage all of the tickets that are being created by the clients. The IT Support Company that this database is designed for can easily look at all the tickets in one place and see what needs to be finished. This is fit for purpose as it is exactly that the company is looking for and the database that I created is the solution. The database is not too complicated as the company is very small and they do not have many clients. Having said this, managing the database is very easy as the forms are well presented and easy to navigate through.
Justification of Features Used
Forms
Forms are very useful when you want employees in your company to edit the database without going into the tables which can end up someone making a mistake. Forms can also be easy to look at depending on how well the forms are designed. It can be easy for someone who does not know how to use Microsoft Access to easily use it by using easy-to-use forms.
Validation Rules
Validations rules allow for only a certain value to be entered in a certain field, record or both. Validation rules help greatly with errors in the database as without these rules, people could misspell the word, or some employees may put capital letters while others leave it as lower case. Having a validation rule will minimise the risk of errors especially when multiple employees will be using the database and it is not just one person. If the employees follow the system, then the database will look neat and error-free.
Macros
Macros are essential to making a database easy-to-use. Having macros to do all the tedious task that doing it manually will take a long time. Macros are useful to save time and make working in the database as efficient as possible.
Buttons
Buttons, just like macros, make everything easier when using the database, increasing efficiency and minimising the risk of error. Buttons are also useful to make a good UI interface with forms, so employees can easily navigate to where they want with a simple click of a button.
Queries
Queries are excellent for finding information you need quickly. If your company asked you to print of tickets that has been created in the last week, then queries would be the best option for that.
Reports
Reports are a great way to display information such as queries that you can print out. Instead of making your own word document trying to make a report that looks good, the reports on the database automatically input the information you need for you. If you ran a query and wanted to print out the results, using the report feature in the database is efficient and effective way to do so.
Suggestions for Improvements
I have been told to improve the user interface a bit more to further increase the usability and easy-to-use design I am going for. To do this, I needed to add a switchboard to easily navigate to each form and back again.
To create the switchboard, I needed to make a new form. Instead of creating a pre-existing form based on the table selected as we did before, I am going to create a blank form to work on. Upon creation of the blank form, I started to create a button in which when you click it, it will open a form.
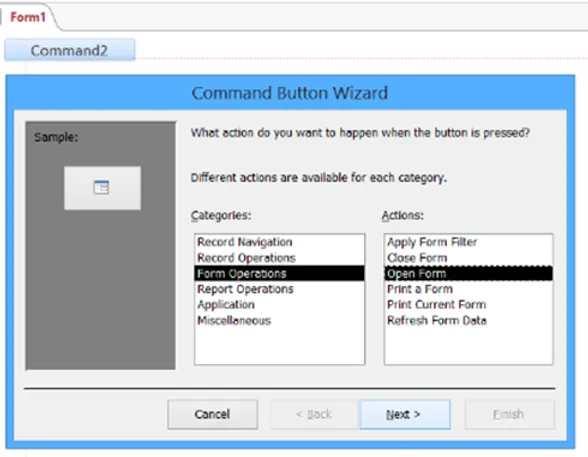
For the first button, I am going to make the button open the ClientCompanyF form.
I edited the text on the button itself to display ‘Client Company’ and I called the button itself ‘ClientCompanyF’.
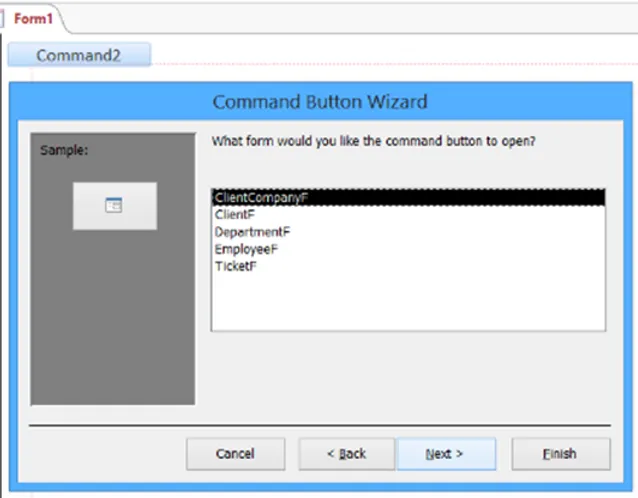
I did this for all the forms that are in my database.
This is the result of the switchboard:
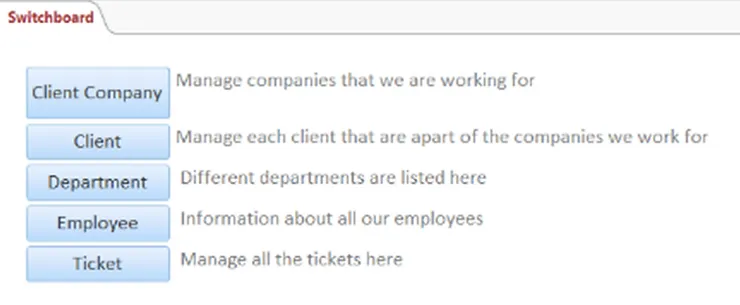
I have correctly added all the buttons which takes me to each form. I have also put a little description next to each button to describe what it is.
As you can see, clicking the ‘Employee’ button will take me to the employee form:
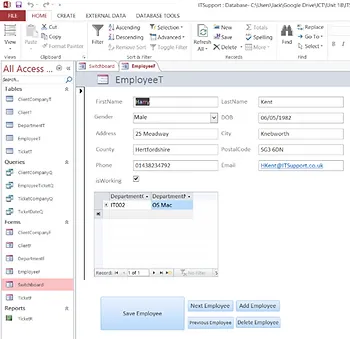
I can then close this form which will take me back to the switchboard for me to navigate to another form.