· Jack Young · Education · 7 min read
Unit 34 (P4): Internal and External Finance
Describe sources of internal and external finance for a selected business.

Describe sources of internal and external finance for a selected business
Describe sources of internal and external finance for a selected business (P4)
Internal Sources
Owner’s Savings
An owner’s savings is money that is generally generated by part of an income which you decide not to spend it on goods and save it in a bank account specifically for savings. Tesco would put their savings into a bank account to then use the money to invest and use it for something they choose such as giving loans to other companies. Depending on how much money is in the savings account will affect how much the money will have interest. The more money in the account, the more interest it will get.
Capital from Profits
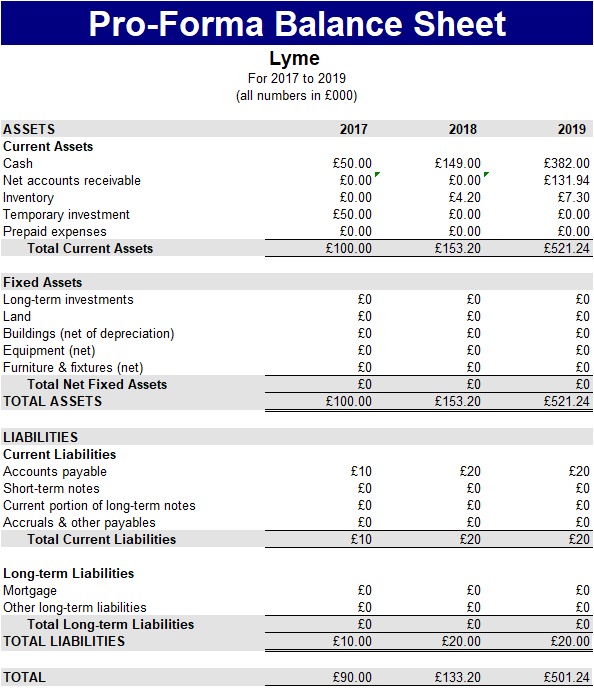
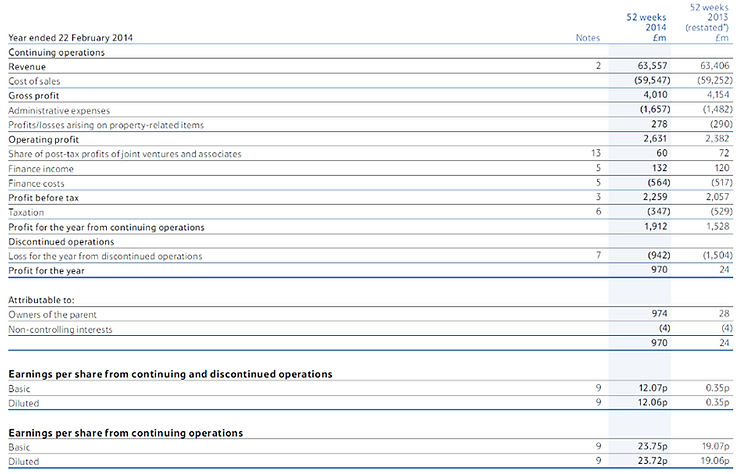
Another internal source is profit. Profit is the additional money that is made on goods that is the result by subtracting the sell price (Inflow) by the initial cost to buy the goods (Outflow). This then would make the gross profit which is already taxed. Tesco would need to use this money to pay for taxes and loans etc. The result of this is called the net profit. The net profit is the reaming money after all the necessary pay-outs (loans and tax have been given out to all the shareholders). The gross profit is what the company would release and say whether they have made a profit or a loss that year. A company like Tesco would give the gross profit at the end of every tax year.
The money that Tesco makes must pay corporation tax which would mean that some of the money that they have made would be taken away (this is the net profit as stated earlier). In addition to this, Tesco would want to retain some of the money. This would mean that the shareholders would be getting less money because Tesco will be paying cooperation tax instead and rationing the money.
External Sources
Overdraft
An overdraft is money that a person would use that is not there money. There is a limit of how much money you can take from an overdraft. The limit of the overdraft is set by the bank. This money does not have a contract like a loan and can be borrowed at any time during the mouth. The AER is very high which would mean that they would have to pay 30-40% back as well as the money borrowed. If it is not paid back, then it is put onto the next month.
Tesco would use an overdraft when they are ordering a large batch of products and if they go over the budget set by the financial team, then they have claim an overdraft to pay for the rest of the products. Tesco can they pay off the overdraft once they have made profit from the products that they sold.
You can set a time scale and choose an amount of money you want to borrow (as long it is within the limits) of an overdraft. This would mean that they would have a certain amount of time and money to pay the overdraft back. Therefore, this would mean that Tesco would be able to pay any money back they borrowed to give back to the bank. Once the money is paid back, then Tesco would not need to give the bank any more money, unless Tesco decides to get another overdraft.
Business Loan
A business loan is like an overdraft in that you borrow money. This time, you can borrow a lot more money from the bank that the simple limits of approx. £100 overdraft could not. Tesco would need to agree with the bank lending them the money how long they will have it for before they pay back. This agreement is signed by the bank and the business making the loan. When the deadline of the signed loan approaches, the business would need to pay this back. This would mean that out of the money that Tesco makes in profit, they would need to pay the loan and give back how much they have agreed to pay. This would be taking away from the gross profit and would mean that Tesco would be able to afford to pay for the loan from the money that they have made. A business loan can be a long or a short term depending on how much money the business is borrowing and how long they would be willing to pay back over a certain amount of time.
Commercial Mortgage
A commercial mortgage is a loan that is placed on a commercial property. Tesco would have a commercial mortgage on their shops that they have across the UK. If something were to happen to a building that has mortgage on it, then Tesco can claim insurance to repair it. The commercial mortgage is only for retail and businesses. The mortgage rate will cost no more than 75% and therefore, this would mean that Tesco would have to pay this to ensure that the building is paid for and insured.
Venture Capital
Venture capital is where a business-like Tesco would invest to start-up a business or help fund an existing small business that wish to expand but needs the money to. This is a short-term affect which will give the small business a boost to improve and become effective. Tesco would be willing to take a risk and invest in such business because if those business become successful, then Tesco can earn a massive return on their investments.
Hire Purchase
A hire purchase is basically where you buy a room for example and you hired to use that room on a certain date for business purposes, then you pay for that room on the date and time you wanted to use it. Tesco can pay for it whenever they want as long as it is within the limits of the hire who is managing this purchase. So if Tesco does not have enough money within their budget to get a room but they need it urgently for a meeting, then they can use the room and pay for it at another time. A hire purchase may be used by Tesco when they hire a room or an office to work in or do meetings. This would mean that they would use the facility for business purposes which would mean that they would have to pay a fee for using it.
Leasing
Leasing is when a business rents a property owned by another business. Depending on the time the business agrees to rent it for, payment is usually on a regular basis such as a week or a monthly basis at a certain amount of money agreed by both businesses. The businesses who agree with these terms have to stand by their terms to keep the lease valid. Tesco would offer this to small businesses to help them to start up or expand their business that they may have a lease on some of their properties to have a place to work.
Factoring
Factoring is where payment from customers comes a lot quicker, so Tesco can receive money quicker, so they do not go into debt. Usually without factoring, it takes a couple of months for a payment to go through and be accepted. However, what a factoring company does is collect customer invoices and pay how much money the invoice is directly to the company. Factoring is done so that Tesco does not sell everything on one day and get the money a few months later, because during this time, Tesco are unable to order more stock because they do not have the money to. Factoring stops Tesco going into debt by getting Tesco to receive money quicker.
Share Issues
Share issues is where the shares in a business become available for other businesses to buy. This is done on an annual basis as if Tesco is making a lot of money then the share that Tesco makes available would increase and businesses would buy the shares because they have increased which means that they will benefit from this. If businesses who buy these shares become successful, then Tesco can get a certain share in the profit they have made.