· Jack Young · Education · 10 min read
Unit 34 (P6, M4): Budgets
A budget is a guideline in which it manages cost over a certain period of time.
Costs and Budgets
Illustrate the use of budgets as a means of exercising financial control of a selected company (P6)
Costs Managed to Budget
A budget is a guideline in which it manages cost over a certain period of time. By establishing a budget, it enables a business like Tesco to identify how much they are spending, how much money they can spend and what to invest the money towards. If Tesco created a budget and identifies the areas in which they are making a profit from, Tesco can look at their budget and invest money in more of those profitable areas if they are able to spend more money. The purpose of a budget is simply to allocate amounts of money to different areas and monitoring the business throughout the year to avoid loss or overspending. Budgeting impacts crucial financial business decisions to ultimately make profit overall for the business.
The advantage of managing a budget is that it makes employees aware of the available costs that they are able to spend. This helps departments within the business communicate and focus on the task without going over budget. It also helps managers of a business to make business decisions and solve problems that they may have.
The disadvantage of budgets is that it takes time to produce. Also, if there is any inaccuracy in the information, then the budget will be wrong and employees will think that that can spend a certain amount of money but the budget overestimated and it is less, this can result in either too much money is spent, or too little, which can affect the profit of the business.
Fixed Costs
Fixed costs are costs that the business have to pay that do not change over a short period of time. As the product sale or service increases, the costs stay the same. The same amount of money is paid regardless of the level of production. Fixed costs can include insurance, rent, electricity, gas, telephone bills and advertising etc.
Variable Costs
Variable costs are costs that the business have to pay but it is possible that they can change as output increases. Variable costs can include raw materials, delivery costs or packaging costs etc.
Monitoring Budgets and Variances
Because a budget is an estimate of future, the businesses actual performance should be similar to the budgeted amounts. Having said this, the actual performance will never exactly be the same as the budget. It will come close, fall short, or exceed the budget. That is why businesses need to monitor the budget, some of these questions you should ask yourself when monitoring the budget:
- How close did the business come to the budgeted figures?
- What adjustments should be made to the current years’ budget?
- What adjustments should be made to budgets in future years?
- What changes should be implemented to improve performance?
The budget should be monitored on a regular basis throughout the year: quarterly, monthly, or even weekly. Consistently reviewing the budget will help you identify problems before they cost the business too much time or money. How often you review the budget depends upon your confidence in the figures and the risk associated with not meeting the budget. For example, if you must meet a certain budget in order to meet your loan obligations, the risk of falling short is high. You should review the budget often in order to assure that the business is on track.
Variance is the difference between budgeted and actual figures. Variance it calculated by subtracting budgeted from actual. Doing this will give two possible outcomes, favourable or adverse. A favourable budget variance refers to positive variances or gains; an unfavourable budget variance describes negative variance, meaning losses and shortfalls. Budget variances occur because businesses are unable to predict the future with complete accuracy. As a result, some variance should be expected when budgets are created.
Why Costs need to be controlled to Budget
Analyse the reasons why costs need to be controlled to budget (M4)
If Tesco does not control costs to budget, then their profits will be affected. This means that Tesco needs to manage their budgets so they are aware of what they can spend.
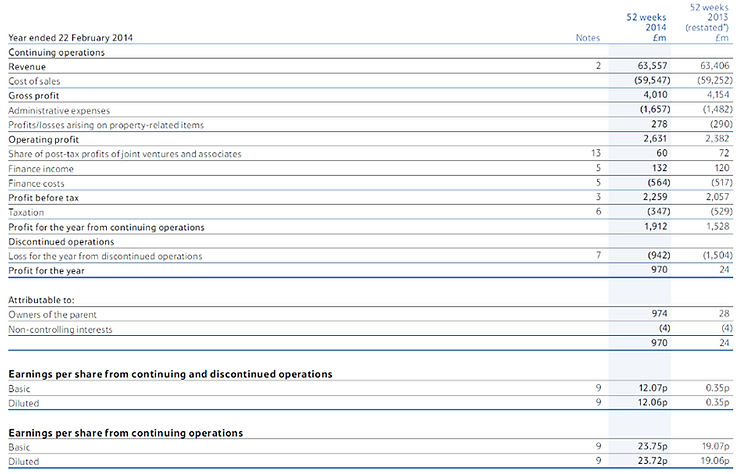
One problem occurs if costs are not controlled to budget is a high fixed cost per item. If the business does not control their cost to budget then they will over or under spend, both of these will result in a loss in profit. If a business does not control their budget effectively and make it so that manufacturing the product is expensive, this may go over the manufacturing budget. If it costs a lot to produce the product, then in order to make a profit, you would need to also increase the sales price. This will result in less people being interested in the product as it may be too expensive and will result in a drop in revenue. Costs need to be controlled to budget as if you have a lower fixed cost per item, then you will be able to manufacture more and ultimately sell more. Tesco has managed their costs to budget effectively in this case as their revenue totals £63,557 and the costs to manufacture was £59,547, so Tesco has made profit rather than a loss because they managed their costs effectively.
Another problem occurs if costs are not controlled to budget is poor cash flow. Poor cash flow is where there is more outflows then inflows which is also caused by poor budgeting. In a result of costs not being controlled to budget, then the business would need to find a way to increase the inflow to balance the outflow. For Tesco, their net liabilities came to a total of negative £5,827 million which means that they spent more on liabilities and borrowing than the assets could produce money. Due to this, Tesco has to use extra money to pay for the costs of the liabilities such as debts. What Tesco can do to solve this is that they can lease what they need like machinery and they can also collect debts on time so they do not spend more on interest. Another way to make more inflow is by making offers on the products they sell. Costs need to be controlled to budget as if the business was aware of how much they can earn and spend, then they can use costs appropriately and control the cash flow.
It is important that both fixed and variable costs are controlled to budget as it is very important aspect of finance in any business. Tesco manages its costs effectively as they produce a financial statement every year which includes everything needed in a budget. Tesco can sometimes make mistakes with their budget, but overall, Tesco does not have many problems as explained above because Tesco controls their costs to budget. If Tesco did not control costs to budget, then it would result in these problems occurring.
Break-even
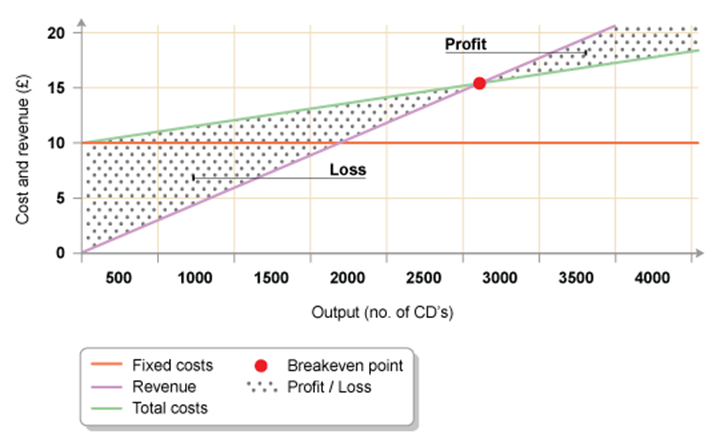
Businesses should aim to break even to ensure that they are going to be financial stable for the future. Break-even is where the business does not make enough sales to make a profit but they make enough sales to avoid making a loss. The point of break-even is shown on a graph that businesses produce to see how well they are doing financially.
The break-even chart below is an example found on BBC Bitesize. This chart shows that a business has a fixed cost of £10,000 (red line) and the variable cost of £2 per unit of CD’s sold. To calculate the variable cost, you do the variable cost per unit multiplied by the number of units. For example, the variable cost per unit is £2 and there are 3000 units. This gives the value of £6,000 in cost. The green line is the total costs once you add the fixed cost to the variable costs. The fixed cost is £10,000, so this value plus the variable cost of £6,000 at 3000 units gives the total cost (green line) of £16,000 at 3000 units (output of CD’s). The green line tells you how much you need to spend to manufacture/produce the product or whatever the business is selling.
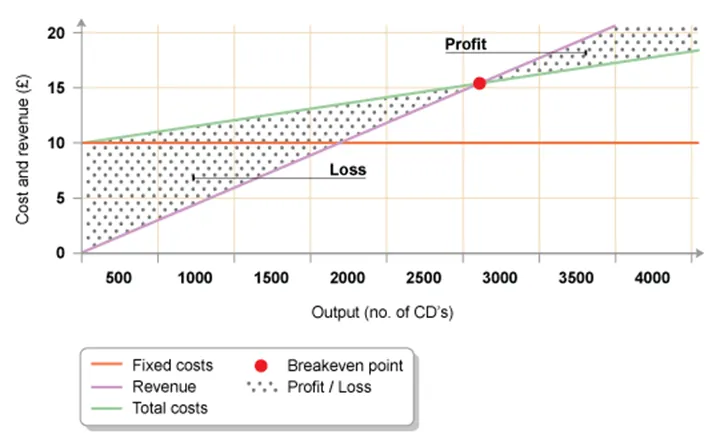
The purple line is the revenue that the business is going to get if they sell units at a certain sales price. The purple line can vary depending on how much the sale price of each unit is. The higher the unit, the steeper the graph which means that you will reach the profit sooner. Having said this, as a break-even chart is a prediction graph of what might happen, then increasing the sales price may not necessarily be the best option as theoretically, no one is going to buy a CD at the sales price of £20 etc. So, when making the sales price, it needs to be reasonable. The purple line given below is the sales price of £6. In order to reach break-even point, the business needs to sell about 2900 units of CD’s. Depending on how well the business does in previous years, this can decide on whether the sales price of a CD being £6 a good option or not. If the business in previous years sold well over 2900 units of CD’s before, then clearly they may have a chance of reaching the break-even point and making profit and not a loss.
Bidding to Increase Future Resources
Sometimes businesses realise that they do not have enough money available in their budgets to, for example, expand or buy new equipment. Therefore, businesses may choose to bid for additional funding through a capital grant or ask others to invest in their business. This means that the business gets to use the money invested by another business and in return, offer a percentage stake in the business. A private limited or public limited company like Tesco may choose to do this by offering shares.
Other businesses that do not have investments from large businesses or do not want other big businesses to be involved; they need to raise money in other ways to fund for their business and they may choose to go to their bank for a loan or may try to raise finance by getting a grant. Grants can be given to businesses by national or local government agencies for many different reasons, including where the business is located, how big the business is or if the business is in an industry that has problems.
Provision of Appropriate Liquidity/Working Capital
Working capital is the day-to- day money needed to pay the bills so the business can remain trading. It is the difference between the current assets that the business has and its current liabilities.
A working capital is extremely important to businesses because it puts them into a position where they can pay their bills. The measurement that shows how easily a business can turn its assets into cash to pay its debts is known as liquidity. The higher the level of liquidity, the easier it is for the business to access extra funds and be able to pay off any debts that it has.
Provision of Appropriate Reserves to Address Emergencies/Crises
Businesses have to make sure that they keep some money at the end of every month in case an emergency should happen. This ensures that if they do have problems, such as an unexpected expense, or there is a downturn in their market due to world events or a natural disaster, they have enough funds to continue in business.
It is also important for businesses to have some reserves in the early stages of their budget planning as it may be difficult to make accurate budget predictions and costs, and income calculations may need to be adjusted. An emergency budget will keep extra funds to allow for additional expenses.